Core Principles
In low-energy beam scenarios (keV ~ hundreds of MeV), reducing the material content of detectors to minimize beam energy loss (beam heating) and directional perturbations (multiple scattering), while maintaining monitoring accuracy, is a critical development direction for non-destructive beam monitoring detectors.
This solution is based on the Micro-Mesh Gaseous Detector (Micromegas), which holds significant potential in beam non-destructive monitoring due to its advantages in radiation resistance, high temporal and spatial resolution, high counting rate, low medium density, and cost-effectiveness.
By modifying the anode readout structure of traditional Micromegas detectors—replacing the solid FR4-based PCB board with a hollowed-out design and integrating a low-mass flexible polyimide material to form the readout-sensitive region—this structural innovation reduces the material content in the sensitive area while preserving Micromegas' high temporal/spatial resolution and high counting rate.
Additionally, the gas chamber sealing film in the Micromegas detector's sensitive region adopts a single-sided aluminum-coated film with a thickness of **<20 μm**, further reducing the overall material content along the beam path.
Product Introduction
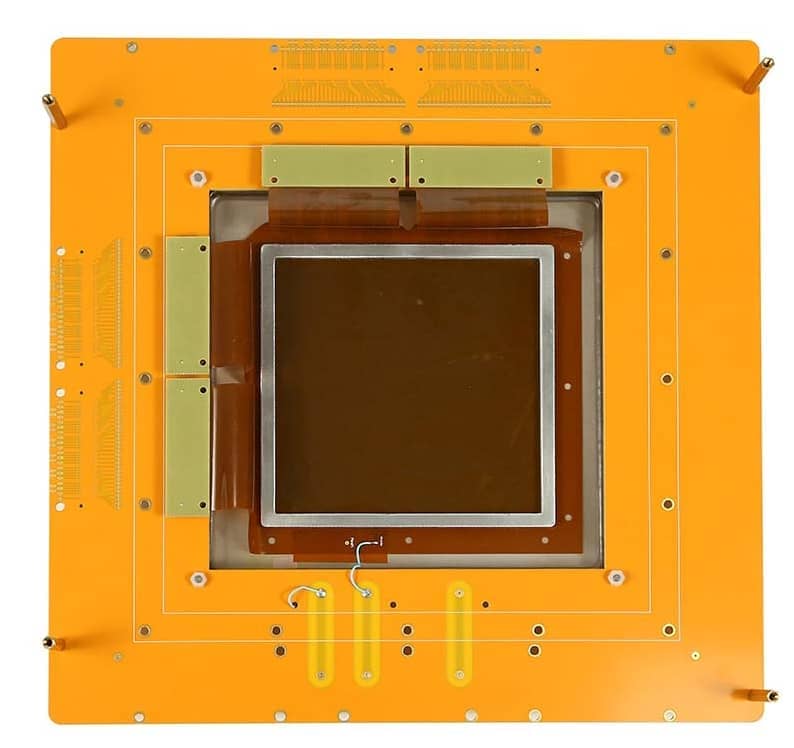
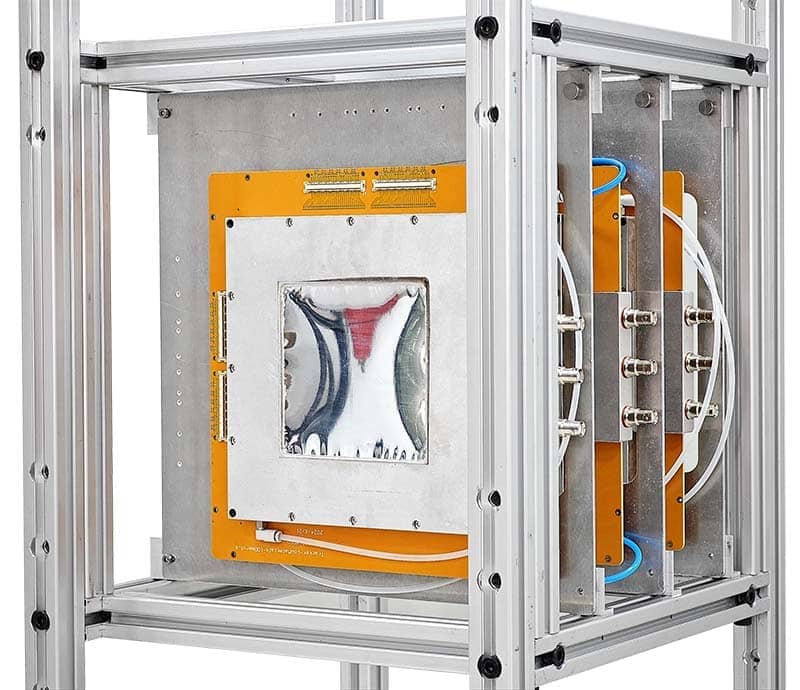
Technical Parameter
1. Material budget: < 0.25% χ₀
2. Active area: 100x100 mm² with 400 um pitch
3. Spatial resolution: <100 um

